NPS vs PPF Return Rates, Comparison, Which is Better? Saving money is a crucial habit to develop if you want to ensure your financial future. But simply allocating a portion of one’s income as savings and letting it lie idle is not sufficient, especially in light of inflation and rising living expenses. To recognize the worth of such money, it is also necessary to choose an appropriate conduit for it. This is where the National Pension Scheme and Public Provident Fund begin, which offer tax advantages, guaranteed returns, and sovereign support to help investors.
Read: What is the Public Provident Fund (PPF)
Read: What is National Pension Scheme, Benefits, Eligibility
The most important financial objective for every individual should be to save for retirement. Consider making long-term, consistent, small deposits as the best method of retirement savings. Two popular solutions for this are the Public Provident Fund (PPF) and the National Pension System (NPS). These two are well-liked retirement savings plans in India. Both are long-term investment possibilities with favorable income tax benefits.
What is the NPS (National Pension Scheme)?
The Central Government launched the National Pension Scheme (NPS) as a social security program. Employees from the public, private, and even unorganized sectors, except those in the armed forces, are eligible for this pension system.
To guarantee all Indian residents’ retirement income security, the National Pension System (NPS) was launched on January 1st, 2004. The central government, state governments, employees of the business sector, and even self-employed professionals can open accounts under this defined contribution pension plan.
The program encourages participants to contribute to a pension account regularly while they are still employed. In this scheme, some part of the total deposited amount may be withdrawn by the subscriber after retirement, while you will get a monthly pension from the remaining sum after your retirement.
Return Rate of The NPS Scheme
The contributions made to the scheme and the selected asset classes determine the returns or interest from the National Pension System. As a result of the money being invested in both debt and shares, the returns on NPS investments are market-linked. The interest is applicable depending on the subscriber’s choice of asset class and the quantity of their contribution.
The NPS program also provides the advantage of tax savings in addition to the benefit of post-retirement financial protection. For people who wish to protect their retirement period and build a long-term financial cushion, this is one of the most rewarding investment options, with a current NPS interest rate of 9%–12%.
What is PPF (Public Provident Fund)?
A public provident fund, which offers tax advantages, guaranteed PPF returns, and sovereign support, might help the investors.
It is a saving program that the Indian government offers to all residents who are Indians, including workers, students, self-employed people, and retirees. A Public Provident Fund account has a lock-in term of 15 years, and according to PPF regulations, the account holder must make deposits each year.
PPF is a long-term investment strategy that is well-liked by people who desire to generate substantial yet reliable returns. The primary goal of those who open a PPF account is the proper protection of the principal sum. When a PPF account is opened, the applicant is assigned a PPF account where money is deposited monthly and interest is accumulated.
For those with a low tolerance for risk, a public provident fund system is perfect. Since the government has authorized this program, it is supported by guaranteed returns to meet the basic financial demands of the Indian public, as its return is not based on market performance.
Return Rates for PPF
The PPF return rate, which is based on the rate of returns on government bonds, is revised by the Indian government every three months. The Indian government has raised the return rate for PPF to 7.1% for the first quarter of the financial year 2023. Account holders must receive their refunds from the Indian government.
Monthly interest calculations are performed for PPF. However, after each fiscal year, such interest is added to the account’s balance.
To calculate interest for a given month, the lowest amount in a PPF account as of both the month’s end date and its fifth day is taken into account.
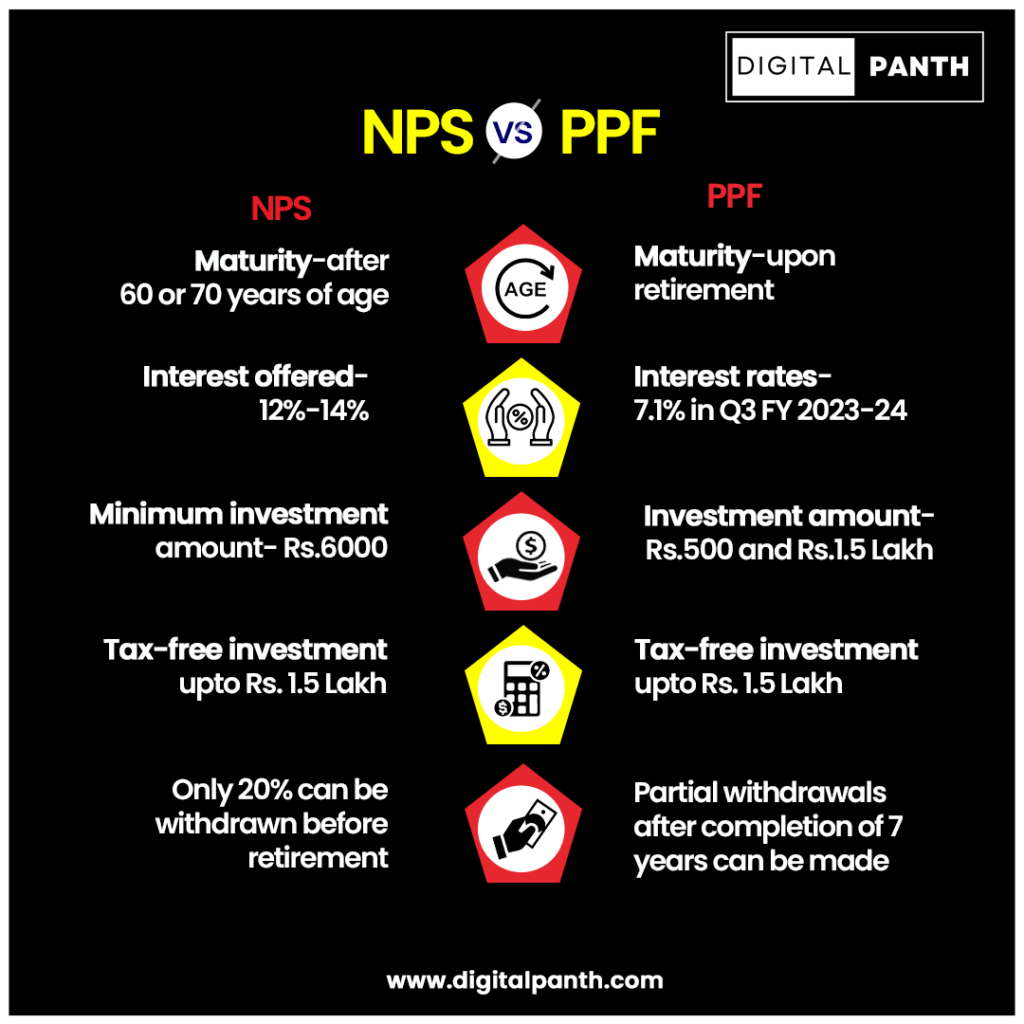
Comparison Between NPS vs PPF
Making a comparison between PPF and NPS is necessary to comprehend the specifics of each product.
A comparative description is given of the PPF and NPS to make it easier for you to decide which investing option is ideal for you.
1- Both Are Government Schemes.
The Government of India introduced the NPS, a market-dependent pension savings program, to help financially disadvantaged retirees. The market and the effectiveness of the pension fund manager therefore influence NPS return rates.
PPF is an instrument that is supported by the government and is not just for pensions; it also has set returns.
2- Investment Limit
In the PPF scheme, the minimum amount allowed for investment is ₹500 and the maximum limit is ₹1.5 lakh annually.
In NPS, the minimum investment amount is ₹6,000 annually, and there is no maximum limit for investing in an NPS account.
3- Eligibility
PPF investments are open to Indian citizens. A person is only permitted to have one PPF account unless the following account is in the name of a minor.
Investors in NPS must be Indian citizens between the ages of 18 and 70. NRIs may also make investments in NPS.
4- Taxation
An investment in a PPF up to the amount of Rs. 1.5 lakh will qualify for a tax deduction under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. According to a statement in the annual income tax return, PPF interests are not subject to taxes. Additionally, the PPF maturity amount is tax-exempt. Investors in PPFs will thus benefit from lax taxation.
Moreover, Section 80C allows for tax deductions on NPS contributions up to Rs. 1.5 lakh. The minimum contribution amount is 10% of your pay. 40% of the NPS balance may be withdrawn without incurring any taxes once the NPS has reached its maturity period. After retirement, the monthly income must be obtained by purchasing an annuity with the remaining 40%. You can take the remaining amount after paying the tax.
5- Withdrawal Facility
The National Pension System (NPS) is avoided by investors due to its restrictive structure, among other factors. Only 60% of the corpus can be withdrawn when your money is locked until you are 60. A monthly pension is generated by investing the remaining 40%.
Since the Public Provident Fund is supported by the central government and there is little possibility of capital loss, it is one of the safest investment options. The benefit of compounding is yet another strong element of PPF. PPF subscribers stand to gain significantly from Public Provident Fund returns because of compounding and a lengthy (15-year) term.
6- Safety
NPS returns are market-dependent and typically not regarded as a secure choice. In this scheme, your return will be directly impacted by market ups and downs. The effectiveness of a pension fund manager is also a factor in determining NPS returns. As a result, you can change managers if you’re unhappy with their performance.
Regarding PPF returns, it is well known that they have fixed returns, so one can essentially rule out any default risk.
7- Return
The return given to subscribers in NPA varies because it depends on the performance of the market.
On the other hand, the return on PPF is fixed and calculated every month.
Which is Better NPS vs PPF?
Any investment tool has advantages and disadvantages. PPF produces set returns in the fixed-income category, but equity pension funds offered by NPS have the potential to produce higher returns over the long run. PPF investments, on the other hand, carry less risk than NPS investments, which are market-based.
Additionally, if you fall into a higher tax bracket, investing in NPS will let you build a tax-efficient retirement fund.
PPF investments might not be a good choice for you if you have less than 15 years until retirement. To secure your funds, NPS can still assist you in building a retirement corpus.
One can choose an investing strategy based on the type, goal, and level of risk-taking of the investor.
Conclusion
Living a long life is likely to result in a greater pension benefit in retirement. To achieve long-term financial security, you don’t have to give up your existing standard of living. When you save, invest, and spend, it requires that you make a deliberate choice to be thrifty with your money.
For a happy and successful later life, having a well-rounded retirement plan is just as important as eating well. One reliable long-term budgeting principle is the 50/30/20 rule of thumb. 50 percent of the budget should go towards essential costs such as mortgages, rent, energy, and food.
It is advised that you spend 30 percent of your income on extracurricular pursuits like vacationing, shopping, and taking care of your health. The remaining 20% should be allocated to investments, savings, and retirement. Your available funds for investments increase as your debt decreases.
Debt reduction is a must. If there are any charges for entertainment, travel, or shopping that can be cancelled or reduced, review your credit card statements for such charges. Keep an eye on the accuracy of your pension statements. You could want to increase your retirement savings or begin investing more in preparation for a lengthy life span.



Leave feedback about this